A Comprehensive Guide to Standard Operating Procedure
Have you ever pondered how a chef consistently recreates a dish with the exact flavor each time it’s ordered by a customer? Likewise, how does Apple maintain consistent iPhone quality, regardless of the factory or country where production takes place? Ensuring that your business processes run seamlessly and efficiently is pivotal for staying competitive and achieving sustainable growth. One powerful tool in achieving operational excellence is the creation of Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs).
Standard Operating Procedures, often abbreviated as SOPs, are step-by-step guidelines that document the best practices for carrying out various tasks within an organization. These procedures are meticulously crafted to ensure consistency, quality, and efficiency in executing specific business processes. The SOPs are paramount, especially when dealing with complex tasks that must adhere to stringent quality and regulatory standards.
SOPs are not confined to a specific sector or industry; they are ubiquitous and find their relevance across various domains. From agriculture to manufacturing, insurance to finance, and beyond, SOPs are a cornerstone of operational excellence.
Why Are SOPs Essential for Your Business?
- Consistency: SOPs provide a standardized framework that ensures every task is performed consistently, irrespective of who is handling it. This consistency is vital for maintaining product or service quality.
- Efficiency: By detailing the most efficient way to complete a task, SOPs can significantly improve productivity and reduce wasted time and resources.
- Training and Onboarding: SOPs serve as invaluable training resources for new employees, enabling them to quickly grasp their roles and responsibilities.
- Internal Controls & Risk Management: SOPs are integral to effective internal controls and risk management within an organization. By following SOPs, companies can mitigate risks associated with human error, fraud, and non-compliance with regulations. Moreover, SOPs help in the identification of potential risks and vulnerabilities within processes, enabling proactive risk management strategies to be put in place.
- Compliance and Accountability: SOPs help businesses adhere to industry regulations and standards. They also establish accountability by clearly defining who is responsible for each task.
- Monitoring and Improvement: What you don’t monitor, you cannot improve. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) play a pivotal role in the monitoring, auditing and improving a processes. By following SOPs, teams can establish benchmarks and track performance over time, facilitating the identification of areas that require improvement.
- Effective Governance: SOPs also aid in the efficient allocation of resources, reducing the likelihood of conflicts and ensuring that governance structures function smoothly. By providing a structured framework for operations, SOPs enable organizations to align their actions with their strategic objectives, maintain compliance, and uphold ethical standards, thus promoting trust and confidence among stakeholders.
General Principles of Standard Operating Procedures
- Clarity and Precision: SOPs should be clear and precise, leaving no room for interpretation or ambiguity. Use straightforward & simple language and avoid jargon or technical terms that may not be universally understood. What is the point of having an SOP that people find difficult to understand and interpret?
- Conciseness: Keep SOPs concise by focusing on the essential steps and information. Unnecessary details can clutter the document and make it less user-friendly.
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent format and structure across all SOPs within the organization. This uniformity aids in ease of use and understanding.
- Practicality: SOPs should be practical and feasible to implement in real-world scenarios. Avoid overly complex or theoretical instructions that may not be applicable.
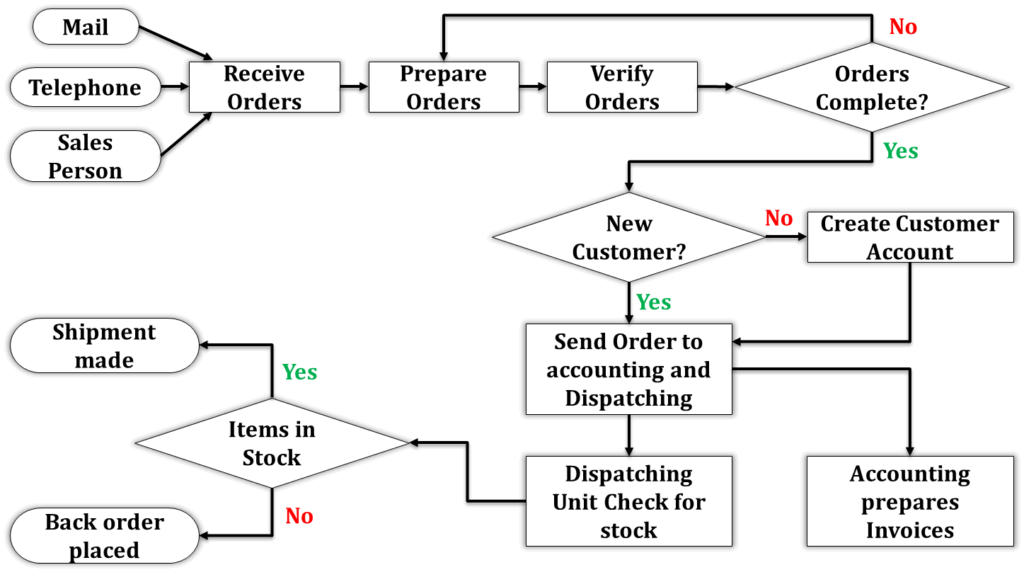
- Visual: A picture is worth 1000 words. Visual or pictorial SOPs are easily understood and grasped as compared to the verbal SOPs. Therefore, use techniques like flow charts, shadow boxes, Kanban Board, Andon etc. to visually communicate with employees.
What to include in the Standard Operating Procedures?
In Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), the level of detailing can vary significantly based on the complexity of the process or task being documented. Here’s an overview of what to include in SOPs and how the level of detail can vary:
- Process Title and Purpose: Begin with a clear and concise title that defines the process or task. Explain the purpose of the SOP to provide context.
- Scope and Applicability: Define the scope of the SOP, outlining which departments or roles it applies to. Specify when and where the process occurs.
- Responsibilities: Clearly state who is responsible for executing each step of the process. This ensures accountability.
- Definitions and Acronyms: Include a glossary of terms and acronyms to eliminate ambiguity and ensure everyone understands the terminology used.
- Materials and Equipment: List all necessary materials, tools, and equipment required for the process. This is particularly important for complex processes that involve specialized tools.
- Safety and Compliance: Detail safety precautions, regulatory requirements, and any legal considerations. For complex processes, this section may be extensive due to various safety measures.
- Procedure Steps: This is where the level of detail varies the most based on complexity:
- Simple Process: For straightforward processes, provide a step-by-step breakdown with clear instructions. The level of detail may be minimal.
- Moderate Complexity: For processes with some intricacies, explain each step comprehensively. Use bullet points or numbered lists for clarity. Include expected timeframes and potential issues.
- High Complexity: Complex processes demand a detailed, in-depth explanation of each step. Use flowcharts, diagrams, or visual aids to illustrate intricate sequences. Include contingencies for various scenarios.
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Specify any forms, logs, or records that need to be maintained during the process. Explain where and how to store documentation.
- Quality Control and Inspection: Describe how quality is monitored, and inspections are conducted. This is especially important for complex processes where precision is critical.
- Performance Metrics: Including performance metrics, their definition and calculation methods in Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) is essential for measuring the effectiveness of a process. These metrics provide quantifiable data that allows organizations to track progress, identify bottlenecks, and continuously improve their operations.
- Troubleshooting and Problem Resolution: Include a section on identifying common issues and how to address them. Complex processes may require an extensive troubleshooting guide.
- Training and Onboarding: Explain how employees are trained in this process. For complexity, include details about training materials, duration, and assessment methods.
- Revision and Approval Process: Outline how the SOP is reviewed, revised, and approved. Complex processes may require more layers of review.
- References and Attachments: Provide links or references to related documents, manuals, or external resources. For complex processes, these references may be numerous.
- Version Control: Maintain a clear version history to track changes and ensure that employees are using the latest version of the SOP.
- Conclusion and Signatures: Summarize the SOP, and include spaces for relevant personnel to sign and acknowledge their understanding and commitment to following it.

Tips for Writing Effective SOPs
Creating SOPs that truly make a difference in your operational efficiency requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here are some tips to help you write SOPs that stand out and drive excellence:
1. Identify the Process: Begin by clearly identifying the specific business process for which you are creating an SOP. Define the process scope and boundaries to avoid confusion.
2. Involve Key Stakeholders: Collaboration is key. Involve the employees who are directly responsible for executing the process. Their input can provide invaluable insights into the nuances of the task.
3. Detailed Step-by-Step Instructions: Break down the process into individual steps. Use clear and concise language, and consider using numbered lists for easy reference. Each step should be actionable and easy to follow.
4. Include Visual Aids: A picture is worth a thousand words. Consider including diagrams, flowcharts, or images to complement your written instructions. Visual aids can enhance comprehension, especially for complex processes.
5. Address Common Challenges: Anticipate potential roadblocks or challenges that employees might encounter while following the SOP. Offer solutions or troubleshooting guidance where necessary.
6. Review and Feedback: Don’t consider your SOPs set in stone. Regularly review and update them based on feedback and changing circumstances. This ensures that your procedures remain relevant and effective.
7. Formatting and Organization: Organize your SOP in a logical sequence. Use clear headings and subheadings to facilitate easy navigation. Consistency in formatting is essential for readability.
8. Compliance and Safety: If the process involves compliance requirements or safety measures, clearly outline these in the SOP. Ensure that all procedures align with legal and safety standards.
9. Training and Testing: Before finalizing your SOP, conduct training sessions with employees to ensure that they can successfully execute the process. Testing the SOP in a real-world scenario can reveal any gaps or issues.
10. Document Management: Implement a robust document management system to keep track of SOP versions, revisions, and who has access to them. This is crucial for maintaining data integrity.

SIPOC Model for Documenting Standard Operating Procedure
Out of various techniques or templates for documenting SOPs, SIPOC model is my favorite. SIPOC stands for Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers. Here’s how it can be applied to SOP documentation:
1. Suppliers:
- Identify the sources or suppliers of inputs needed for the process.
- This could include internal departments, external vendors, or other stakeholders.
- Document their roles, responsibilities, and contributions to the process.
2. Inputs:
- List all the materials, information, or resources required to initiate and execute the process.
- Specify the quality standards and expectations for these inputs.
- Detail where and how these inputs are obtained or generated.
3. Process:
- Describe the step-by-step sequence of activities within the process.
- Include all relevant tasks, responsibilities, and decision points.
- Use clear and concise language to explain how the process works.
4. Outputs:
- Define the end results or deliverables produced by the process.
- Specify the quality criteria and standards that the outputs must meet.
- Indicate where these outputs are sent or how they are used in subsequent steps.
5. Customers:
- Identify the recipients or customers who receive and use the process outputs.
- Describe their needs, expectations, and any specific requirements.
- Consider both internal and external customers and their roles in the overall process.
By applying the SIPOC model to SOP documentation, organizations can gain a holistic view of their processes, ensuring that all relevant stakeholders, inputs, and outputs are considered. This aids in creating comprehensive and effective Standard Operating Procedures that contribute to operational excellence.
Conclusion
Creating effective Standard Operating Procedures is a vital step toward achieving operational excellence in your business. By following these tips, you can craft SOPs that not only streamline your processes but also contribute to the overall success of your organization.
Remember, the key to success lies in meticulous planning, clear communication, and a commitment to continuous improvement. So, go ahead and start writing SOPs that will set your business on the path to excellence.



